How to Determine Current Rating (Amperage) of a BusBar?
A busbar (or a bus bar) is a key component in electrical power distribution, acting as a central connection point for multiple circuits. Proper rating of a busbar is essential to ensure safe and efficient power transfer, particularly in high-current applications such as marine, automotive, and industrial electrical systems. This article examines key factors in determining busbar ratings, including material selection, ampacity, environmental considerations, and standard guidelines.
Key Factors in determining BusBar Rating:
1. Conductor Material Selection
The material composition of a busbar directly affects its conductivity and heat dissipation. The most commonly used material is copper, specifically Tin-Plated Copper C11000, due to its high conductivity and resistance to oxidation. Alternatives like brass is less conductive and may require increased cross-sectional areas to compensate for their lower efficiency. Additionally, the material should be corrosion-resistant and galvanically compatible with the conductor and terminal lugs, as specified in ABYC E-11.15.5.1.
2. Insulation base Material
Like electrical cables, the higher temperature the insultation next to the conductors can endure, the larger current the cable or busbar is allowed to carry. For example, an 8AWG single conductor cable (cross section area around 8.4 mm²) is rated 65A with insulation rated at 75°C. However, a cable with same 8 AWG (8.4 mm²) conductor would be rated 80A if its insulation is rated at 105°C. In YIS Marine we use mostly Glass Fiber reinforced Nylon 66 (PA66+GF), which has more than 200°C deformation temperature, as bus bar insulation base and this would ensure busbars of the same conductor size have best current rating in the market.
Busbar Current-Carrying Capacity (Ampacity) Calculation:
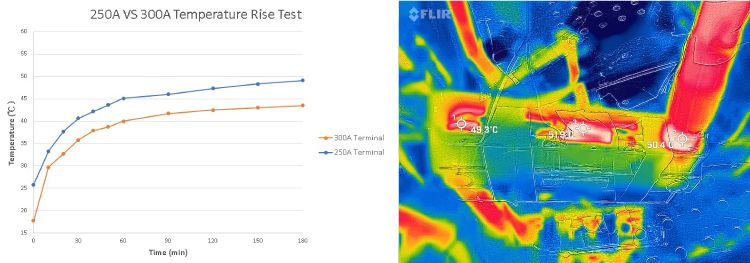
1 Temperature rising test (IEEE method)
Up until late 2010's, there were no consistent way to determine the rating of a busbar. The old way is to utilize temperature rising tests of a busbar to determine its maximum rating. According to Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) guideline:“a busbar should be rated at the highest amperage passing through any section of the busbar, with a maximum of a 50° C rise in temperature from an ambient temperature of 50° C.”
Therefore manufacturers could determine busbar rating by applying rated amperage current to the busbar in an ambient temperature of 50°C in field test and see if anywhere of the busbar exceeds 100°C (50°C + 50°C) to make sure if the busbar is capable of carrying that current.
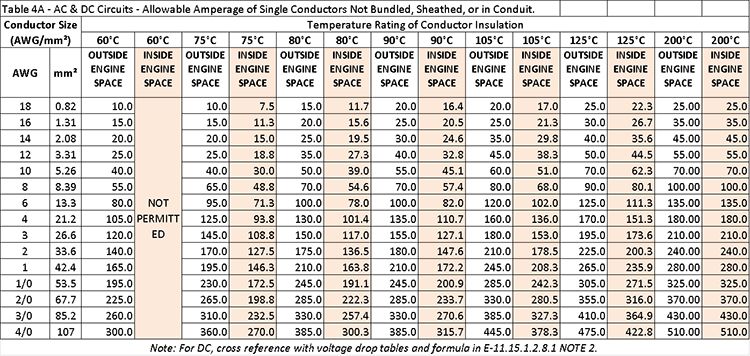
2. Cross-sectional area reference chart (ABYC)
More recently, ABYC (The American Boat & Yacht Council) has added a section in E11 (E11.15.5) to identify the suitable cross-section area for suitable rating for a busbar. In short, the ampacity (current-carrying capacity) of a busbar is determined by its cross-sectional area (deducted by half the diameter of holes drilled in its conducting path), the insulation temperature rating, and whether it is intended to be installed inside or outside engine space, by referencing to Table 4A – 4D in ABYC E11. Below is an example Table (4A) of conductors vs allowable amperages in ABYC E11 (2021 Edition).
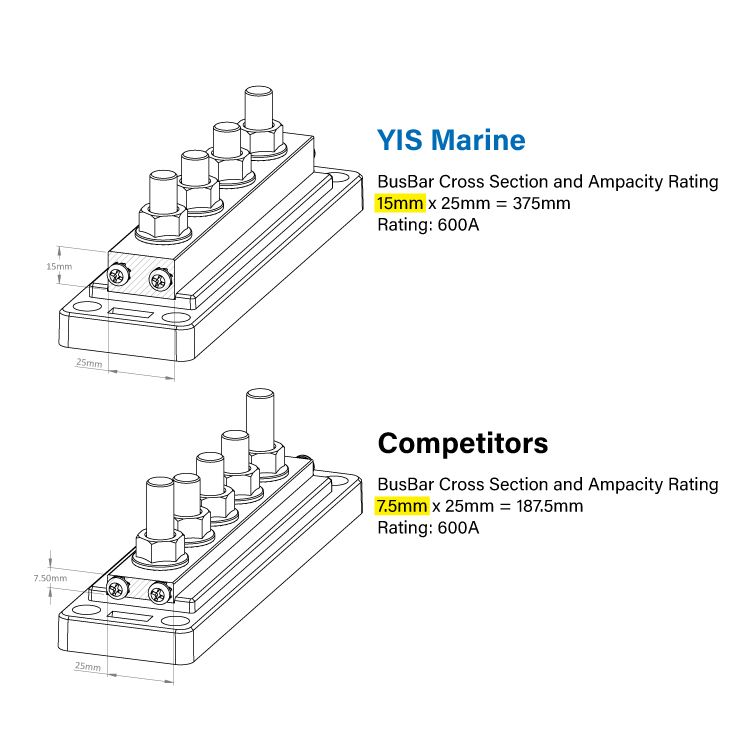
Please note that even if the published rating is the same, busbar can be designed with very different cross section area by different manufacturers – resulting in very different temperature rising results. This not only applies to busbars but also other products like fuse blocks or switch panels with internal buses.
Other design considerations
Except for the current rating of a busbar, there are other factors to consider in designing a proper bus bar in marine or caravan environment:
1. Insulation and short circuit protection
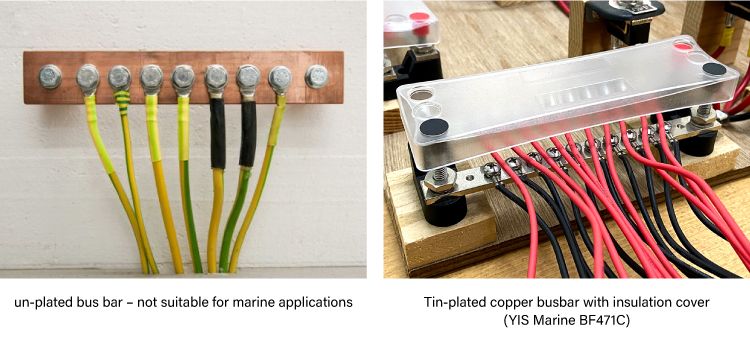
Busbars need to be protected from short circuiting and environment contamination if they are not intended to be used as DC or AC grounding bus. Busbars with insulation covers are a good means of solutions.
2. Spacing
Busbars should be spaced at least 0.1 inch (2.54mm) from the mounting surface and use nonmetallic insulation that can withstand the expected operating temperature.
3. Anti-corrosion
Busbars used in marine or industrial environments must withstand exposure to moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations. Aluminum or un-plated steel is not allowed to use in marine environment. Electrical plating like Tin-plating or Nickel plating is also often necessary to prevent oxidation and corrosion, particularly in high-humidity areas.
4. Fasteners
Traditionally manufacturers would use two nuts and a spring washer on busbar studs to fix the cable ring terminals, this however often misled users to install ring terminals in between the two nuts and / or place one nut and the spring washer in between conducting path. Nuts and spring washers are mostly made of (stainless) steels and are not suitable for conducting currents, so bad installations putting nuts and washers between the ring terminals and busbar would often cause excessive heat and high temperature. Modern busbar design often incorporates single flange nut (without washer) which eliminates the chance of bad installation.
Choosing the right busbar rating is crucial for safe and efficient power distribution. By considering material selection, ampacity, installation environment, and compliance with safety standards, you can ensure a durable and reliable electrical connection. At YIS Marine, we design and manufacture high-quality busbars engineered up to standard for marine and industrial applications. Our products are rigorously tested to meet industry standards and provide customization options for specific power distribution needs. Contact our team today for expert guidance on selecting the right busbar for your application.
- Related Products
Dual Bus Bar
BF204
Dual busbar in brass material to allow 60A cumulative amp max. Available from 2 gang to 8 gang.
DetailsLarge Current Bus Bar
BF207
Large current busbar in copper material to allow 150A cumulative amp max. Only available with...
DetailsHeavy Duty Bus Bar Box
BF432 (M10, M8) / BF432R (M10, M8)
Heavy duty busbar box with four terminal studs (M10 or M8). With the box length being exact...
DetailsHeavy-Duty Bus Bar Box
BF433 / BF433R
Heavy duty busbar box with 2x M10 terminal studs & 6x M5 screws. With the box length being...
DetailsHeavy Duty Dual Bus Bar Box
BF434 / BF434R
Heavy duty busbar box with removable connecting link. With the box length being exact two times...
DetailsSingle Bus Bars
BF421 (6P, 12P)
Single busbar in brass allows 100A the most, available with 6 gang and 12 gang. Optional transparent...
DetailsDual Bus Bars
BF422 (6P, 12P)
Dual busbar with removable connecting link in brass allows 100A the most, available with 6 gang...
DetailsSingle Bus Bars
BF423 (4P, 6P)
Single busbar in brass allows 100A the most, available with 4 gang and 6 gang. Optional transparent...
DetailsCommon Bus Bars
BF424 (10P, 22P)
Standard common busbar allows 150A the most, available with 10 gang and 22 gang. Optional transparent...
DetailsSingle Bus Bars
BF425 (6P, 12P)
Single busbar in copper allows 150A the most, available with 6 gang and 12 gang. Optional transparent...
DetailsDual Bus Bars
BF426 (6P, 12P)
Dual busbar with removable connecting link in copper allows 150A the most, available with 6 gang...
Details“2-Steps” Dual Bus Bar
BF427 (6P, 12P)
2-step dual busbar with different heights allows more flexible wiring, available with 6 gang...
DetailsMini Bus Bars (100A) - (Imperial Threading - Upgraded 2020)
BF471(2020) | BF471M (5P)
Mini busbar with imperial threading screws and studs allows 100A the most. Optional insulation...
DetailsMini Bus Bars (100A) - (Imperial Threading - Upgraded 2020)
BF472(2020) | BF472M (4P)
Mini busbar with imperial threading screws and studs allows 100A the most. Optional insulation...
DetailsCommon Bus Bars (150A) - (Imperial Threading - Upgraded 2020)
BF473(2020) | BF473M (10P)
Common busbar with imperial threading screws and studs allows 150A the most. Optional insulation...
DetailsCommon Bus Bars (150A) - (Imperial Threading - Upgraded 2020)
BF474(2020) | BF474M (4P)
Common busbar with imperial threading screws and studs allows 150A the most. Optional insulation...
DetailsCommon Bus Bars (150A) - (Imperial Threading - Upgraded 2020)
BF475(2020) | BF475M (20P)
Common busbar with imperial threading screws and studs allows 150A the most. Optional insulation...
DetailsCommon Bus Bars (150A) - (Imperial Threading - Upgraded 2020)
BF476(2020) | BF476M (6P)
Common busbar with imperial threading screws and studs allows 150A the most. Optional insulation...
DetailsCommon Bus Bars (150A) - (Imperial Threading - Upgraded 2020)
BF477(2020) | BF477M (12P)
Common busbar with imperial threading screws and studs allows 150A the most. Optional insulation...
DetailsMaxiPower Bus Bar (300A) - (Imperial Threading - Upgraded 2020)
BF478(2020) | BF478M (4P)
Heavy Duty copper bus bars carry current up to 300A
DetailsMaxiPower Bus Bar (300A) - (Imperial Threading - Upgraded 2020)
BF479(2020) | BF479M (6P)
Heavy Duty copper bus bars carry current up to 300A
DetailsMaxiPower Bus Bar (300A) - (Imperial Threading - Upgraded 2020)
BF480(2020) | BF480M (12P)
Heavy Duty copper bus bars carry current up to 300A
DetailsUltra Power Bus Bar (600A)
BF481 (4P)
The Ultra Power Bus Bar by YIS Marine is a top-tier solution that combines durability, efficiency,...
Details